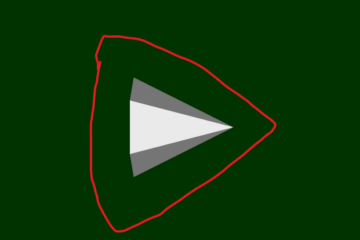
It’s a simple job for us to make bounding box visible in traditional VTK render window.
We can SetCurrentRenderer for renderWindowInteractor->GetInteractorStyle() and press P to show it.
#include <iostream>
#include <vtkSmartPointer.h>
#include <vtkSphereSource.h>
#include <vtkActor.h>
#include <vtkConeSource.h>
#include <vtkRenderer.h>
#include <vtkRenderWindow.h>
#include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h>
#include <vtkProperty.h>
#include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h>
#include <vtkLight.h>
#include <vtkCamera.h>
#include <vtkOBBTree.h>
#include <vtkActor2D.h>
#include <vtkMath.h>
#include <vtkTransform.h>
#include <vtkTransformFilter.h>
#include <vtkMatrix4x4.h>
#include <vtkInteractorObserver.h>
#include "tool.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
setbuf( stdout, nullptr );
vtkSmartPointer<vtkConeSource> cone =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkConeSource>::New();
cone->SetDirection( 1, 1, 0 );
cone->Update();
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> mapper =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New();
//mapper->SetInputData( polydata );
mapper->SetInputData( cone->GetOutput() );
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> actor =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New();
actor->SetMapper( mapper );
vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer> renderer =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderer>::New();
renderer->AddActor(actor);
renderer->SetBackground( 0, 0, 0 );
vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow> renderWindow =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindow>::New();
renderWindow->AddRenderer( renderer );
vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor> renderWindowInteractor =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkRenderWindowInteractor>::New();
renderWindowInteractor->GetInteractorStyle()->SetCurrentRenderer( renderer );
renderWindowInteractor->SetRenderWindow( renderWindow );
renderer->ResetCamera();
renderWindow->Render();
renderWindowInteractor->Start();
return 0;
}
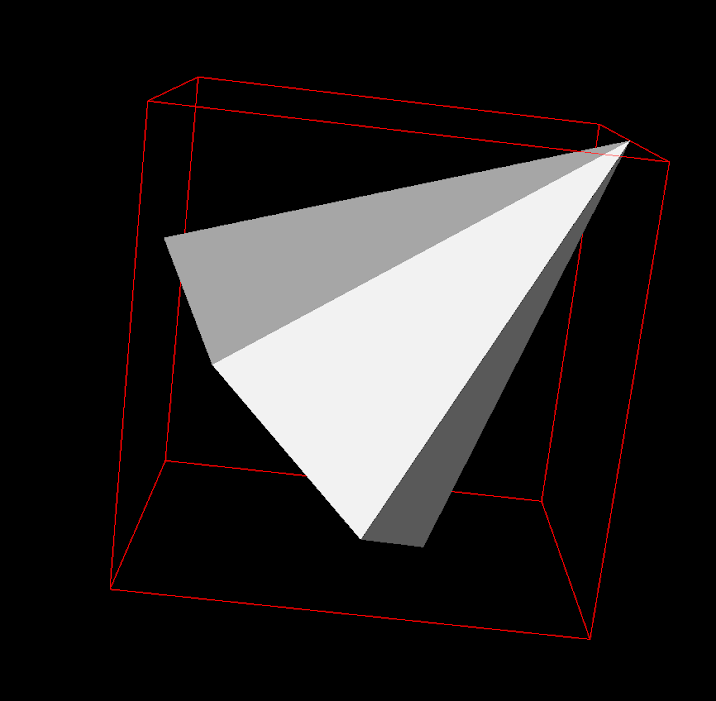
vtkOutlineFilter
We can use vtkOutlineFilter and vtkPolyDataNormals to draw a bounding box and show by vtkActor.
// --------------------- start to draw bounding box ------------------------
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataNormals> normals =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataNormals>::New();
normals->SetInputConnection( cone->GetOutputPort() );
vtkSmartPointer<vtkOutlineFilter> outlineFilter =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkOutlineFilter>::New();
outlineFilter->SetInputConnection( normals->GetOutputPort() );
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> outLinemapper =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New();
outLinemapper->SetInputConnection( outlineFilter->GetOutputPort() );
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> outlineActor = vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New();
outlineActor->SetMapper( outLinemapper );
outlineActor->GetProperty()->SetColor( 1,1,1 );
// --------------------- Drawing bounding box end------------------------
...
renderer->AddActor( outlineActor );
vtkBoundingBox
vtkBoundingBox is a simple class which deals with 3D bounds.
It is not derived from vtkObject.
we can use vtkBoundingBox to calculate bounds points and create box poly data and show it.
vtkBoundingBox boundingBox;
for( int i = 0; i < cone->GetOutput()->GetNumberOfPoints(); ++i )
{
boundingBox.AddPoint( cone->GetOutput()->GetPoint( i ) );
}
double bounds[6] = { 0 };
boundingBox.GetBounds( bounds );
vector<PointStruct> pts;
for( int i = 0; i < 2; ++i )
{
for( int j = 2; j < 4; ++j )
{
for( int k = 4; k < 6; ++k )
{
pts.push_back( PointStruct( bounds[i], bounds[j], bounds[k] ) );
}
}
}
for( auto it: pts )
{
cout << it;
}
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> boundsPolydata =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New();
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints> boundsPoints =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints>::New();
for( int i = 0 ; i < 8; ++i )
{
boundsPoints->InsertNextPoint( pts[i].point );
}
boundsPolydata->SetPoints( boundsPoints );
vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> cells =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray>::New();
vtkIdType cell[2] = { 0, 1 };
cells->InsertNextCell( 2, cell );
cell[0] = 0; cell[1] = 2;
cells->InsertNextCell( 2, cell );
cell[0] = 3; cell[1] = 2;
cells->InsertNextCell( 2, cell );
cell[0] = 3; cell[1] = 1;
cells->InsertNextCell( 2, cell );
cell[0] = 4; cell[1] = 5;
cells->InsertNextCell( 2, cell );
cell[0] = 4; cell[1] = 6;
cells->InsertNextCell( 2, cell );
cell[0] = 7; cell[1] = 5;
cells->InsertNextCell( 2, cell );
cell[0] = 7; cell[1] = 6;
cells->InsertNextCell( 2, cell );
cell[0] = 1; cell[1] = 5;
cells->InsertNextCell( 2, cell );
cell[0] = 0; cell[1] = 4;
cells->InsertNextCell( 2, cell );
cell[0] = 2; cell[1] = 6;
cells->InsertNextCell( 2, cell );
cell[0] = 3; cell[1] = 7;
cells->InsertNextCell( 2, cell );
boundsPolydata->SetLines( cells );
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> boundsMapper =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New();
boundsMapper->SetInputData( boundsPolydata );
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> boundsActor =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New();
boundsActor->SetMapper( boundsMapper );
boundsActor->GetProperty()->SetColor( 1, 0, 0 );
...
renderer->AddActor( boundsActor );
output:
PointStruct [-0.707107, -0.707107, -0.433013]
PointStruct [-0.707107, -0.707107, 0.433013]
PointStruct [-0.707107, 0.353553, -0.433013]
PointStruct [-0.707107, 0.353553, 0.433013]
PointStruct [0.353553, -0.707107, -0.433013]
PointStruct [0.353553, -0.707107, 0.433013]
PointStruct [0.353553, 0.353553, -0.433013]
PointStruct [0.353553, 0.353553, 0.433013]