The copy operation for mat: cv::Mat::clone() or cv::Mat::copyTo().
Most of the copying interfaces are under the reference count mechanism.
All image information is expressed by a single matrix in OpenCV. The tuple (r, g, b) is used by men to watch the colorful world.
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
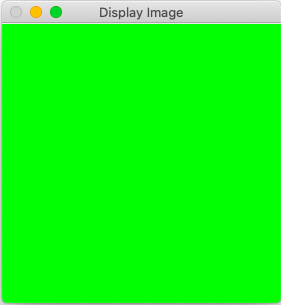
Mat image( 2, 2, CV_8UC3, Scalar(0,255,0) ); // b , g , r
cout << "image= " << image << endl;
namedWindow("Display Image", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
imshow("Display Image", image);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
The constructor in the above code snippet has the following definition.
/** @overload
@param rows Number of rows in a 2D array.
@param cols Number of columns in a 2D array.
@param type Array type. Use CV_8UC1, ..., CV_64FC4 to create 1-4 channel matrices, or
CV_8UC(n), ..., CV_64FC(n) to create multi-channel (up to CV_CN_MAX channels) matrices.
@param s An optional value to initialize each matrix element with. To set all the matrix elements to
the particular value after the construction, use the assignment operator
Mat::operator=(const Scalar& value) .
*/
Mat(int rows, int cols, int type, const Scalar& s);How to define array type:
CV_[The number of bits per item][Signed or Unsigned][Type Prefix]C[The channel number]eg:
Mat image( 2, 2, CV_8UC4, Scalar(0,255,0, 155) ); // b , g , r, transparent