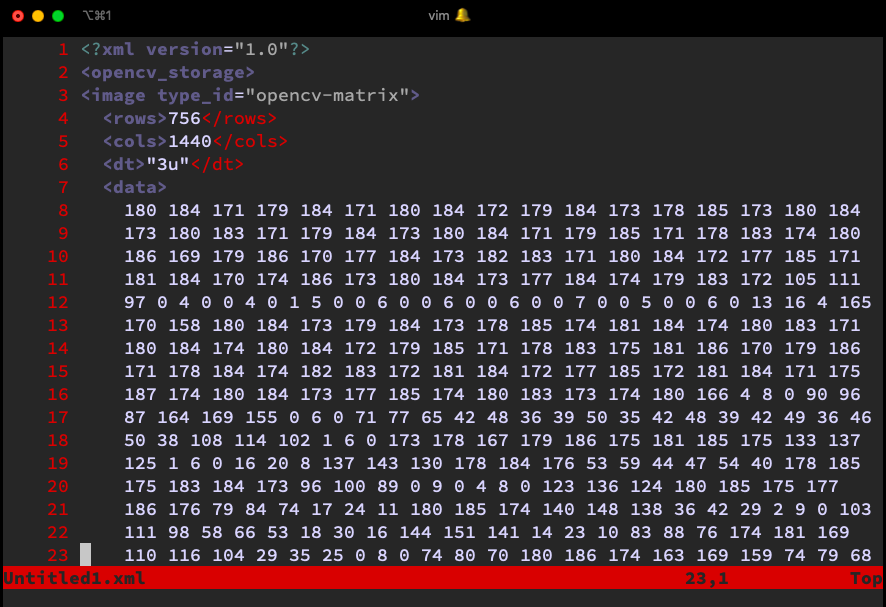
We can use XML to store the OpenCV matrix and read it to recover the whole image.
A simple example is in the following code snippet.
We write an original image data to Untitled1.xml, then read it to generate another Mat object and show it.

#include <stdio.h>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <string>
using namespace cv;
int main(int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat image;
std::string fileName = "/Users/weiyang/Desktop/Untitled1.png";
std::string outName = "/Users/weiyang/Desktop/Untitled1.xml";
image = imread( fileName, IMREAD_COLOR );
if ( !image.data )
{
printf("No image data \n");
return -1;
}
// =============== write ================
FileStorage fs1( outName, FileStorage::WRITE );
fs1 << "image" << image;
fs1.release();
// =============== read ================
FileStorage fs2;
fs2.open( outName, FileStorage::READ );
Mat readMat;
fs2["image"] >> readMat;
std::cout << "readMat = " << readMat << std::endl;
namedWindow("Display Image", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
imshow("Display Image", readMat);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
More using details about XML and YAML can be found in File Input and Output using XML and YAML files