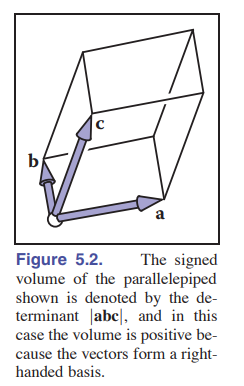
The geometry meaning of the determinant is the sign volumn value for three vectors in 3D world or a sign area value of two vectors (parallelogram) in the 2D coordinate system.
For three points in the 2D world:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[\delta=det\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 \\ x_0 & x_1 & x_2 \\ y_0 & y_1 & y_2 \end{bmatrix}\]](https://www.weiy.city/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-abeb1c2800f2bf3c4ec526dd3b748aa0_l3.png)
The triangle is counterclockwise ordered if ![]() and clockwise ordered if
and clockwise ordered if ![]() . If
. If ![]() , these points are collinear.
, these points are collinear.
For three vectors in the 3D world, It’s sign volumn value for three vectors.
![]()
#include "point.hpp"
#include <vtkSmartPointer.h>
#include <vtkPolyData.h>
#include <vtkMatrix3x3.h>
#include <vtkMath.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Point pt0( 0, 0, 0 );
Point pt1( 0, 1, 0 );
Point pt2( 1, 1, 0 );
// three points are on the same plane
vtkSmartPointer<vtkMatrix3x3> matrix = vtkSmartPointer<vtkMatrix3x3>::New();
double value[3][3] = { { 1, 1, 1 }, { pt0[0], pt1[0], pt2[0] }, { pt0[1], pt1[1], pt2[1] } };
for( int i = 0; i < 3; ++i ){
for( int j = 0; j < 3; ++j ){
matrix->SetElement( i, j, value[i][j] );
}
}
std::cout << "det: " << matrix->Determinant() << std::endl; // det: -1 ; means they are clockwise
pt2 = Point( 0, -1, 0 );
matrix->SetElement( 1, 2, pt2[0] );
matrix->SetElement( 2, 2, pt2[1] );
std::cout << "det: " << matrix->Determinant() << std::endl; // det: 0 ; means three vertices are collinear
// three vectors in the 3D world
pt0 = Point( 0, 0, 1 );
pt1 = Point( 0, 1, 1 );
pt2 = Point( -1, 1, -1 );
std::cout << "det: " << vtkMath::Determinant3x3( pt0.point, pt1.point, pt2.point ) << std::endl; // det: 1; means three vertices are counterclockwise
return 0;
}