I will show a way to export CPlusPlus algorithm to javascript code.
Write Pollard’s rho algorithm in class Resolver for integer factorization.
resolver.h
#include <string>
typedef long long LL;
class Resolver
{
public:
Resolver();
~Resolver();
std::string GetResolvedResult(int x);
protected:
void find(LL n,LL c);
bool Miller_rabin(LL p);
LL Pollard_rho(LL n,LL c);
LL quick_mod(LL a,LL p,LL m);
LL multi(LL a,LL b,LL m);
LL gcd(LL a,LL b);
const int N=6e5;
int cnt;
LL *fac;
LL *num;
};
resolver.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include "resolver.h"
Resolver::Resolver()
{
cnt = 0;
fac = new LL[N];
num = new LL[N];
}
Resolver::~Resolver()
{
delete [] fac;
delete [] num;
}
std::string Resolver::GetResolvedResult(int x)
{
char str[10005] = { 0 };
cnt=0;
find(x,120);
std::sort(fac,fac+cnt);
memset(num,0,sizeof(num));
int k=0;
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++){
if(i==0){
num[k]++;
continue;
}
if(fac[i]==fac[i-1]){
num[k]++;
}
else {
k++;
fac[k]=fac[i];
num[k]++;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
if( num[i] != 1 )
{
sprintf(str + strlen(str), "%lld^{%lld} \\times ",fac[i], num[i]);
}
else {
sprintf(str + strlen(str), "%lld \\times ",fac[i]);
}
}
if( num[k] != 1 )
{
sprintf(str + strlen(str), "%lld^{%lld}", fac[k], num[k]);
}
else {
sprintf(str + strlen(str), "%lld", fac[k]);
}
return std::string( str );
}
void Resolver::find(LL n,LL c)
{
if(n==1) return ;
if(Miller_rabin(n)){
fac[cnt++]=n;
return ;
}
LL p=n;
while(p>=n) p=Pollard_rho(p,c--);
find(p,c);
find(n/p,c);
}
bool Resolver::Miller_rabin(LL p)
{
if(p==2) return 1;
if(p<2 || (p&1)==0) return 0;
LL m=p-1;
int sum=0;
while((m&1)==0){
m>>=1;
sum++;
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
LL a=rand()%(p-1)+1;
LL x=quick_mod(a,m,p);
LL g=0;
for(int j=0;j<sum;j++){
g=multi(x,x,p);
if(g==1&&x!=1&&x!=p-1) return 0;
x=g;
}
if(g!=1) return 0;
}
return 1;
}
LL Resolver::Pollard_rho(LL n,LL c)
{
LL x,y,k=2,i=1;
x=rand()%(n-1)+1;
y=x;
while(1>0){
i++;
x=(multi(x,x,n)+c)%n;
LL d=gcd((y-x+n)%n,n);
if(1<d&&d<n) return d;
if(y==x) return n;
if(i==k) {
y=x;
k<<=1;
}
}
}
LL Resolver::quick_mod(LL a,LL p,LL m)
{
LL ans=1;
while(p){
if(p&1) ans=multi(ans,a,m);
a=multi(a,a,m);
p>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
LL Resolver::multi(LL a,LL b,LL m)
{
LL ans=0;
while(b){
if(b&1) ans=(ans+a)%m;
a=(a+a)%m;
b>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
LL Resolver::gcd(LL a,LL b)
{
return b==0?a:gcd(b,a%b);
}
Use EMSCRIPTEN_BINDINGS() blocks to create bindings for functions to use these methods in WebAssembly module.
Create binding.cpp.
#include <emscripten/bind.h>
#include "resolver.h"
using namespace emscripten;
EMSCRIPTEN_BINDINGS(resolver) {
class_<Resolver>("Resolver")
.constructor()
.function("GetResolvedResult", &Resolver::GetResolvedResult)
;
}
We need to test the algorithm before build these c++ code to wasm. Write main.cpp to test it simply.
#include "resolver.h"
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
Resolver worker;
std::cout << worker.GetResolvedResult( 100 ) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
Now let’s create CMakeLists.txt to build the test CPlusPlus program and WebAssembly module.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Debug)
project(Resolver LANGUAGES CXX)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)
set( Hdrs resolver.h )
set( Srcs resolver.cpp )
if(EMSCRIPTEN)
list(APPEND Srcs
binding.cpp
)
else()
list(APPEND Srcs
main.cpp
)
endif()
if(EMSCRIPTEN)
set(emscripten_options)
list(APPEND emscripten_options
"--bind"
"-O3"
"-g"
"-DLOG_OFF"
"SHELL:-s EXPORTED_RUNTIME_METHODS=['allocate,stringToUTF8,UTF8ToString,intArrayFromString']"
"SHELL:-s -fdebug-compilation-dir=."
"SHELL:-s EXPORT_NAME=createModule"
"SHELL:-s ALLOW_MEMORY_GROWTH=1"
"SHELL:-s DEMANGLE_SUPPORT=1"
"SHELL:-s EMULATE_FUNCTION_POINTER_CASTS=0"
"SHELL:-s ERROR_ON_UNDEFINED_SYMBOLS=0"
"SHELL:-s MODULARIZE=1"
"SHELL:-s WASM=1"
"SHELL:-s --no-heap-copy"
"SHELL:-s INITIAL_MEMORY=200MB"
"SHELL:-s MAXIMUM_MEMORY=4000MB"
"SHELL:-s ASSERTIONS=2"
)
endif()
add_executable(${PROJECT_NAME} ${Hdrs} ${Srcs})
target_compile_options(${PROJECT_NAME}
PUBLIC
${emscripten_options}
)
target_link_options(${PROJECT_NAME}
PUBLIC
${emscripten_options}
)
I will ignore test process, now let’s build wasm file directly.
Create a new folder build_wasm next to CMakeLists.txt and go to inside it.
emcmake cmake ..
emmake make
Then we can get js and wasm files.
CMakeCache.txt CMakeFiles cmake_install.cmake Makefile Resolver.js Resolver.wasm
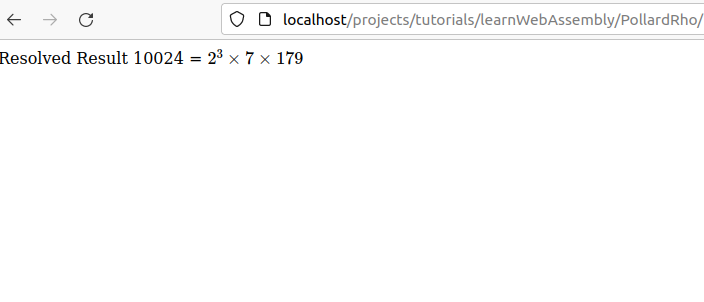
Finally, let’s load the WebAssembly module and show the integer factorization result.
<html>
<head>
<!-- Load WebAssembly module -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="build_wasm/Resolver.js"></script>
<script src="check-for-tex.js" defer></script>
</head>
<body>
<div>
Resolved Result
<span id="answer"/>
</div>
<script>
// Wait for module to initialize,
createModule().then(({Resolver}) => {
const worker = new Resolver();
const x = 10024;
const result = worker.GetResolvedResult( x );
// Write the value of 'root' to the tag whose 'id' is equal to "answer"
console.log( result );
document.getElementById("answer").innerHTML = x.toString() + " = $" + result + "$";
});
</script>
</body>
</html>