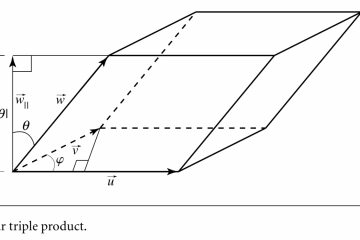
A(B+C) = AB + AC
We defined three different matrix A(m x n), B(n x r), and C(n x r), they satisfy distributivity of multiplication over addtion: A(B+C) = AB + AC.
#include <CGAL/Linear_algebraHd.h>
#include <CGAL/Linear_algebraCd.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace CGAL::Linear_Algebra;
typedef CGAL::Linear_algebraCd<double> LA;
typedef LA::Matrix Matrix;
typedef LA::Vector Vector;
template <typename Type>
Matrix BuildMatrix( int rowCount, int colCount, Type *values )
{
std::vector<Vector> elements;
for( int i = 0; i < rowCount; ++i ){
std::vector<Type> tmp;
for( int j = 0; j < colCount; ++j ){
tmp.push_back( values[i*colCount + j] );
}
elements.push_back( Vector( tmp.begin(), tmp.end() ) );
}
Matrix M( elements.begin(), elements.end() );
return M;
}
int main()
{
CGAL::set_mode( cout, CGAL::IO::PRETTY );
double values0[16] = { 1, 1, 2, 3, // column vector
0, 1, 0, 3,
0, 2, 5, 1,
0, 0, 10, 9 };
auto A = BuildMatrix( 4, 4, values0 );
double values1[16] = { 1, 0, 0, 3, // column vector
0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 5, 1,
3, 0, 0, 0 };
auto B = BuildMatrix( 4, 4, values1 );
double values2[16] = { 1, 0, 0, 2, // column vector
0, 1, 0, 11,
2, 0, 2, 0,
0, 0, 0, 4 };
auto C = BuildMatrix( 4, 4, values2 );
auto tmp = A*(B+C);
cout << tmp << endl;
tmp = A*B + A*C;
cout << tmp << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
LA::Matrix((4, 4 [2, 0, 2, 3,
2, 2, 16, 3,
54, 110, 49, 46,
51, 105, 22, 45,
])
LA::Matrix((4, 4 [2, 0, 2, 3,
2, 2, 16, 3,
54, 110, 49, 46,
51, 105, 22, 45,
])
The transposition of a matrix product
![]()
The transposition of a matrix product is equivalent to the product of the thransposition of every matrix, with the order of multiplication reversed.
int main()
{
CGAL::set_mode( cout, CGAL::IO::PRETTY );
double values0[16] = { 1, 1, 2, 3, // column vector
0, 1, 0, 3,
0, 2, 5, 1,
0, 0, 10, 9 };
auto A = BuildMatrix( 4, 4, values0 );
double values1[16] = { 1, 0, 0, 3, // column vector
0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 5, 1,
3, 0, 0, 0 };
auto B = BuildMatrix( 4, 4, values1 );
auto result = LA::transpose( A*B );
cout << result << endl;
result = LA::transpose( B ) * LA::transpose( A );
cout << result << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
LA::Matrix((4, 4 [1, 1, 32, 30,
0, 1, 0, 3,
0, 10, 35, 14,
3, 3, 6, 9,
])
LA::Matrix((4, 4 [1, 1, 32, 30,
0, 1, 0, 3,
0, 10, 35, 14,
3, 3, 6, 9,
])
The inverse of the matrix product
![]()
int main()
{
CGAL::set_mode( cout, CGAL::IO::PRETTY );
double values0[16] = { 1, 1, 2, 3, // column vector
0, 1, 0, 3,
0, 2, 5, 1,
0, 0, 10, 9 };
auto A = BuildMatrix( 4, 4, values0 );
double values1[16] = { 1, 0, 0, 3, // column vector
0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 5, 1,
3, 0, 0, 0 };
auto B = BuildMatrix( 4, 4, values1 );
double det;
auto result = LA::inverse( A*B, det );
cout << result << endl;
cout << "det: " << det << endl;
result = LA::inverse( B, det ) * LA::inverse( A, det );
cout << result << endl;
cout << "det: " << det << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
LA::Matrix((4, 4 [-0.0224561, -0.0736842, 0.0112281, 0.0245614,
-0.621053, 0.368421, -0.189474, 0.210526,
-0.0378947, 0.0631579, 0.0189474, -0.0210526,
0.340819, 0.0245614, -0.00374269, -0.00818713,
])
det: 1
LA::Matrix((4, 4 [-0.0224561, -0.0736842, 0.0112281, 0.0245614,
-0.621053, 0.368421, -0.189474, 0.210526,
-0.0378947, 0.0631579, 0.0189474, -0.0210526,
0.340819, 0.0245614, -0.00374269, -0.00818713,
])
det: 1
Inverse the product of a number and a matrix
![]() (with a != 0)
(with a != 0)
int main()
{
CGAL::set_mode( cout, CGAL::IO::PRETTY );
double values0[16] = { 1, 1, 2, 3, // column vector
0, 1, 0, 3,
0, 2, 5, 1,
0, 0, 10, 9 };
auto A = BuildMatrix( 4, 4, values0 );
double a = 10, det;
auto result = LA::inverse( a*A,det );
cout << result << endl;
result = (1/a) * LA::inverse(A, det);
cout << result << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
LA::Matrix((4, 4 [0.1, 0, 0, 0,
-0.0621053, 0.0368421, -0.0189474, 0.0210526,
-0.0189474, 0.0315789, 0.00947368, -0.0105263,
-0.0105263, -0.0157895, 0.00526316, 0.00526316,
])
LA::Matrix((4, 4 [0.1, 0, 0, 0,
-0.0621053, 0.0368421, -0.0189474, 0.0210526,
-0.0189474, 0.0315789, 0.00947368, -0.0105263,
-0.0105263, -0.0157895, 0.00526316, 0.00526316,
])